8 Operation
8.1 Operation planning and control
8.1.1 Planning of product supply process (process planning)
The Production Department identifies and plans the product realization process, and the planning shall be consistent with other requirements in the quality management system. The planned output shall be documented in a type suitable for the company’s operations. The document shall specify the input, activity, and output requirements for each process. And the corresponding responsibilities, permissions and resource allocation, if necessary, shall be clear:
a) product quality objectives (indicators) and requirements.
b) requirements for product identification processes (including outsourcing processes), documentation and resources.
c) determine the verification, validation, monitoring, measurement, inspection and testing activities required for the product and the acceptance criteria for the product.
d) records to determine and prepare evidence for the process and conformity of the products
When the production process changes (which may include raw materials, process flow, equipment, product characteristics), the Production Department must review, consider the outcome of unintended changes, and take steps to mitigate adverse effects as necessary.
8.2 Customer’s requirements for products and services
Based on our needs related to customer communication to ensure efficient operations, written procedures are created, implemented and maintained by the Sales Department.
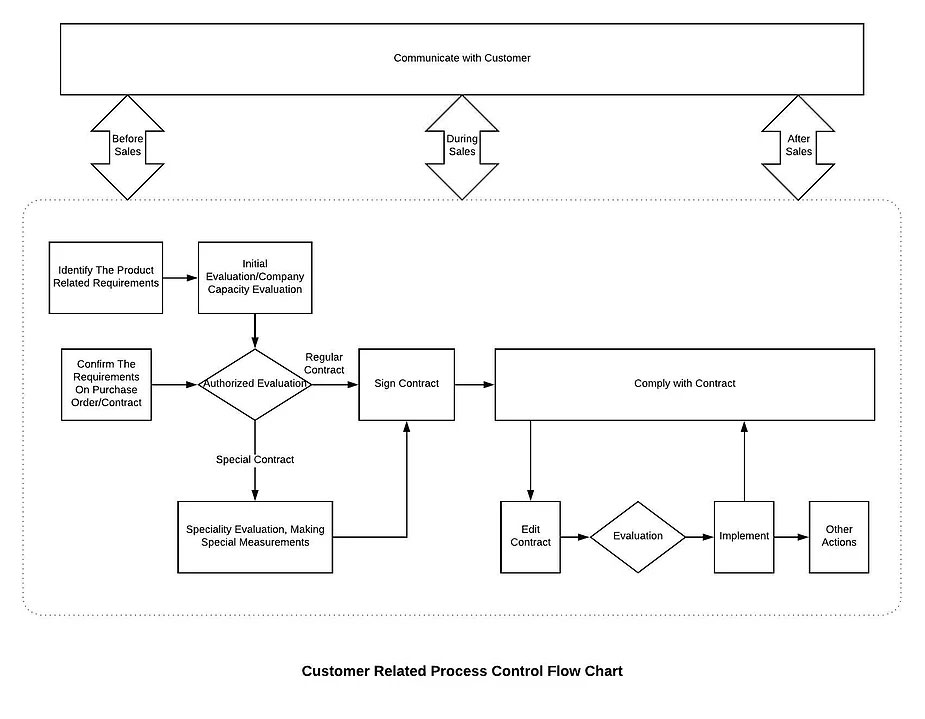
8.2.1 Customer Communication
8.2.1.1 Sales department shall be responsible for communicating with customers about business-related issues. Communication shall be:
a) Multi-level: For example, communication between executive levels or sale departments from each company
b) Multi-channel: For example, communication between salespeople, technicians, and quality control specialists
c) Multi-timing: For example, communication before, during and after sales
d) Multi-method: For example, communicating with customers by visiting, calling and having a questionnaire.
8.2.1.2 Communication with customers shall include:
a) providing information relating to products and services;
b) handling inquiries, contracts or orders, including changes;
c) obtaining customer feedback relating to products and services, including customer complaints and specific requirements for contingency actions, when relevant.
d) handling or controlling customer property
8.2.2 Determining Customer requirements
8.2.2.1 The requirements related to the product refer to the full range of requirements from product requirements to product reuse.
8.2.2.2 The Sales Department shall determine the requirements related to the product from the following perspectives:
a) Customer-defined requirements (such as product quality requirements), including requirements for delivery and post-delivery activities (post-delivery activities include customer contract or any after-sales service identified in the order).
b) Required requirements related to the use, although not explicitly stated by the customer.
c) Requirements of laws and regulations related to the product, including:
d) All regulations applicable to the purchase, storage, handling, recycling, elimination or disposal of materials.
f) Any additional requirements determined by the company (such as additional requirements for factors such as customer satisfaction, the company’s own development needs, and its conditions).
8.2.3 Review of Customer requirements related to the product
8.2.3.1 The review of the requirements related to the customer shall be carried out separately before the bidding phase of the project and before the signing of the contract.
8.2.3.2 The requirements of the review include:
a) Product requirements have been specified (or have been established).
b) The requirement to inconsistent the contract or order with the previous statement has been resolved.
c) The company has the ability to meet the required requirements.
8.2.3.3 The assessment method may be a meeting, a signing or a direct review. Specific execution (related to the customer process control)
8.2.3.4 The conclusions of the review and the tracking measures triggered by the review must be recorded and maintained.
8.2.4 Changes to Customer requirements for products and services When the product requirements change during the target stage or before the contract is signed, the reviewed change information shall be timely transmitted to the relevant departments, personnel, and suppliers to ensure that the relevant documents are modified and the relevant personnel is informed of the change request.
8.3 Design and development of products and services
This is not applicable
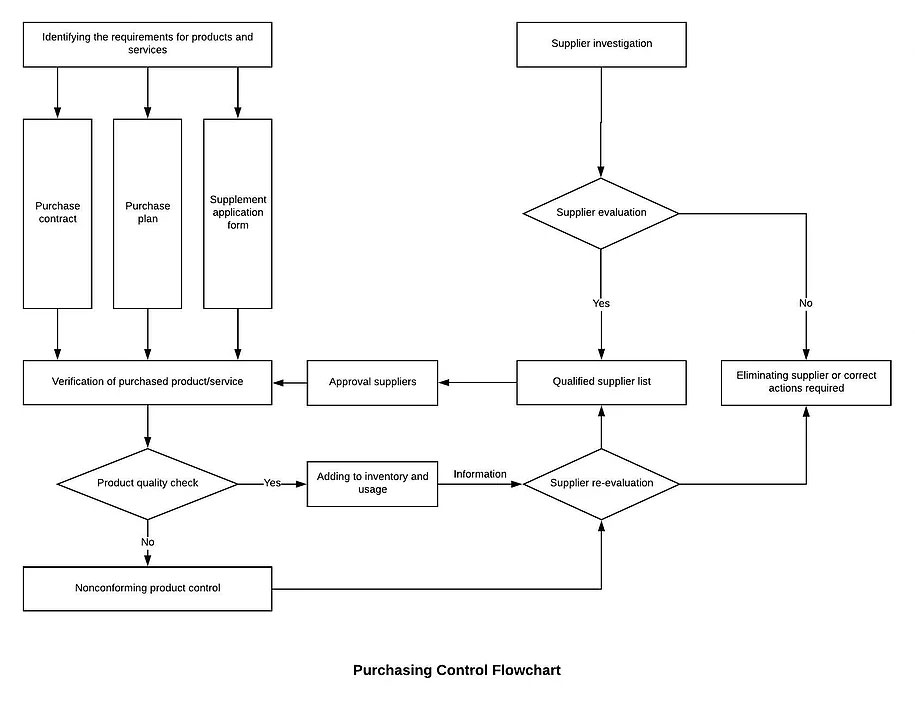
8.4 Control of externally provided processes; products and services
8.4.1 Extent of control and provider management
8.4.1.1 The company’s purchasing control is mainly applied when purchasing various raw materials, and there is no outsourcing process in the production process.
8.4.1.2 The method and procedure for controlling the supplier shall depend on the result of the purchased product on the product realization process and the quality of the final product.
8.4.1.3 In order to ensure that the purchased products meet the requirements, the Purchasing Department shall select, evaluate and re-evaluate the ability of the supplier (including the outsourced supplier) to provide products according to the requirements and guidelines of the supplier evaluation, and evaluate the qualified supply. Who passing the evaluation are listed in the Qualified Supplier List.
8.4.1.4 Any necessary measures arising from the supplier evaluation shall be recorded and maintained.
8.4.2 Type and extent of control
8.4.2.1 The company’s procurement of products, usually using the method of purchase verification by the quality control department.
8.4.2.2 For suppliers whose product quality and delivery time are unstable, the purchaser may verify with the relevant department before the purchase to the supplier’s source, and indicate the verification arrangement and the most release mode in the procurement documents.
8.4.2.3 When the customer requests to the supplier for verification, the purchaser shall also indicate the verification arrangement and the way the product is released in the procurement documents.
8.4.2.4 The verification at the supplier’s source cannot be used as evidence of the supplier’s qualifying product.
8.4.3 Purchasing Information
8.4.3.1 The procurement documents shall specify the name, specification, quantity, delivery date, quality requirements, supplier name, etc., and, if necessary, the approval requirements for the product, the procedure, the equipment, and the qualifications of the personnel provided. And the requirements for the supplier’s quality management system.
8.4.3.2 The Purchasing Department is responsible for implementing the procurement and ensuring that all procurement requirements are adequate and appropriate before communicating with the supplier.
8.4.3.3 The Purchasing Department monitors the performance of external suppliers on a daily basis, such as the approval rate, the timely delivery rate, and the timeliness of rectification of problems, as evidence of the supplier’s annual assessment.
8.4.4 Influence on related parties
8.4.4.1 The Purchasing Department shall carry out an assessment of the necessary environmental occupational health and safety factors in the evaluation/reevaluation of the supplier to determine the manner and extent of the influence of the supplier and other related parties on the environmental occupational health and safety of the company.
8.4.4.2 The Purchasing Department shall, according to the results of the assessment, exert the necessary influence on the supplier that may affect the occupational health and safety of the environment according to the procedural requirements, and give appropriate control.
8.4.4.3 Relevant parties that do not meet the requirements shall take measures to eliminate or reduce the environmental occupational health and safety risks brought to the company and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
8.5 Production and service provision
8.5.1 Control of production and service provision – overview
8.5.1.1 The company establishes and maintains the “production plan control procedures” and “production process control management procedures.” The Technical Department is responsible for the control of the production process, the Production Department is responsible for the management of the production process, and the Sales Department is responsible for the communication after delivery and delivery.
8.5.1.2 Each functional department shall ensure that the company’s production and service activities operate under controlled conditions from the following aspects:
a) provide technical specifications to field operators.
b) set up process documents and work instructions in the required positions. Consider the application of the prevention technology in the process planning process and take measures to prevent human error.
c) use and maintain suitable production, monitoring, and measuring equipment.
d) monitoring of important production and service processes or equipment.
e) analyze the results of monitoring and measurement and make improvements promptly.
f) release and deliver products as required, and provide necessary follow-up services promptly
8.5.1.3 Process Confirmation
8.5.1.3.1 The company shall confirm the special process in production and service. The principle of confirmation is:
a) When the results of the process cannot be verified by subsequent monitoring measurements.
b) The process of the problem after the product has been delivered.
8.5.1.3.2 According to the analysis of L art, the hydrogenation, desulfurization, and polymerization of the production process of the company are processes that need to be confirmed.
a) Specify and approve the production process guidelines.
b) Qualification of production equipment and personnel for these processes.
c) Operate and record in strict accordance with the prescribed process.
d) If the process, equipment, and personnel are changed, the above process should be reconfirmed.
8.5.2 Identification and Traceability
8.5.2.1 The company establishes and maintains the “Marking and Traceability Control Procedures”, and each department shall execute the operations in accordance with the procedures.
8.5.2.2 The production department/warehouse department shall organize and determine the product identification requirements in the whole process of product realization, and determine the appropriate identification methods (such as listing, division, accompanying records, etc.), relevant departments are implemented as required to identify products
8.5.2.3 The quality control department shall determine the inspection status (including qualification, non-conformity, inspection, etc.) of the product identified by the appropriate method (such as listing, accompanying record, etc.) for the measurement and monitoring requirements of the product, and the inspector shall implement it as required.
8.5.2.4 The production department organizes the analysis and determines the requirements for product traceability of the company itself, customers, regulations, standards, etc., and the relevant departments shall control and record the unique identification of the products in the product realization process according to regulations to ensure that the necessary Traceability requirements.
8.5.2.5 Identify and identify related requirements and related reminders such as the environment, occupational health and safety, safety production, social responsibility and counter-terrorism.
8.5.3 Property belonging to Customers and suppliers
8.5.3.1 Customer property mainly includes the customer’s intellectual property (such as the customer’s technical requirements, application sites, etc.) and the tools provided by the customer to verify product conformity, etc.
8.5.3.2 The property of the external supplier mainly includes the packaging of the supplier, which is recycled by the purchasing department according to the agreement of the parties.
8.5.3.3 If there is a technical specification provided by the customer, the sales department shall transfer the production department to control as a foreign document, and refer to the “Document Control Procedure” for details.
8.5.3.4 When the property provided by the customer or an external supplier is found to be lost, damaged or otherwise not applicable, the corresponding department shall record it and The sales department/purchasing department that feeds the counterpart is contacted and negotiated by the counterpart management department.
8.5.4 Preservation of Product
8.5.4.1 Each production and warehouse unit is responsible for the centralized management of product protection (including warehouse, production site and delivery process) of the department.
8.5.4.2 Identify products in accordance with the provisions of the Marking and Traceability Control Procedures to prevent confusion and misuse.
8.5.4.3 Product protection targets include purchased products, semi-finished products and finished products.
8.5.4.4 The product protection requirements shall be fully implemented by marking, handling, packaging, storing and protecting the products according to the regulations at the corresponding stages.
8.5.5 Post-delivery activities The sales department is responsible for determining the scope and extent of the activities after the product is delivered, and the corresponding provisions in the contract, including
a) Legal and regulatory requirements
b) Potential undesired consequences associated with the product
c) the nature, use and life expectancy of the product
d) customer requirements
e) Customer feedback
The sales department is responsible for organizing the implementation, verification and reporting of post-delivery activities and guarantees
a) Ensure that technical documents delivered are controlled and updated
b) Provide sufficient technical support and resources for post-delivery activities, and assign technical personnel to use on-site guidance when needed
c) Collect and analyze information in the delivery
d) When problems are discovered after delivery, appropriate measures (including investigation, processing and reporting) should be taken
Note: Post-delivery activities may include related activities as defined in the warranty terms, such as contractual technical guidance, and recycling or eventual disposal of additional services.
8.5.6 Control of changes to production or service provision
When the process changes, the Production Department is responsible for organizing the review and control of the changes to ensure stable compliance.
The Production Department is responsible for keeping records and information about changes to the process design process, including those who change the results of the review, who are authorized to make changes, and the necessary actions to take in accordance with the review.
8.6 Release of products and services
8.6.1 The Quality Control Department shall establish and maintain the “Monitoring and Measurement Control Procedures” and shall be responsible for the monitoring and measurement of the raw material inspection, process inspection, and finished product shipment inspection to verify that the product requirements have been met.
8.6.2 In the product realization planning stage, the Quality Control Department shall make detailed provisions for the inspection of each stage, compile the corresponding inspection operation documents, and clarify the inspection points, inspection items, frequency, inspection means and inspection rules.
8.6.3 The inspectors at all levels shall complete the inspection work at the corresponding stage according to the requirements of the inspection operation documents.
8.6.4 The inspection results shall be recorded and the inspection records shall be kept. The inspection record shall:
a) Clearly indicate whether the product meets the requirements of the acceptance criteria (patterns, specifications, standards, etc.)
b) Persons entitled to release should sign or affix their seals
c) The product may be released (including delivered) after all inspections have been completed and the inspection results meet the requirements. In special circumstances, the concession of the qualified product shall be approved by the company’s authorized personnel, and if necessary, the customer’s approval is required
8.7 Control of Nonconformances
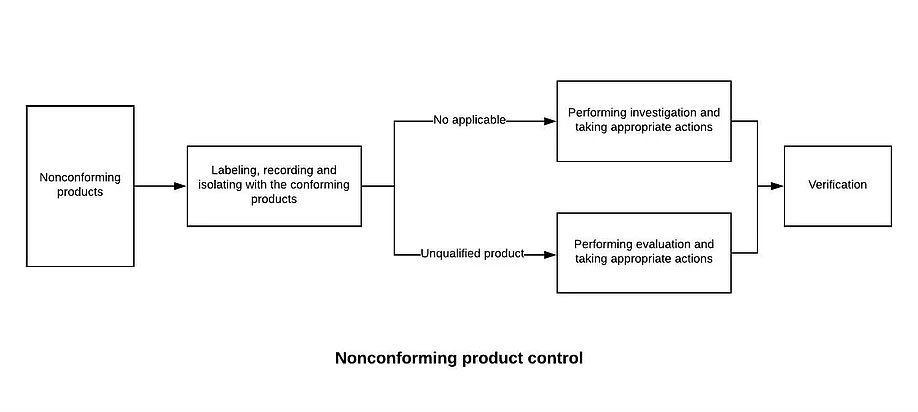
8.7.1 The Quality Control Department shall establish and maintain the “non-conforming product control procedures” to prevent unintended use or delivery of non-conforming products. Disposal of nonconforming product is usually handled by one or more of the following methods:
a) Correction (such as rework), and after correction should be repeated to verify that it meets the requirements
b) quarantine, limit, return or suspend the use of products and services
c) inform the customer
d) obtain authorization to receive concessions
8.7.2 After disposing of the non-conforming product, it is necessary to leave a record including the description of the non-conformity (name, model specification, quantity, non-conforming nature), the measures taken, the concessions obtained and the authorization to dispose of.


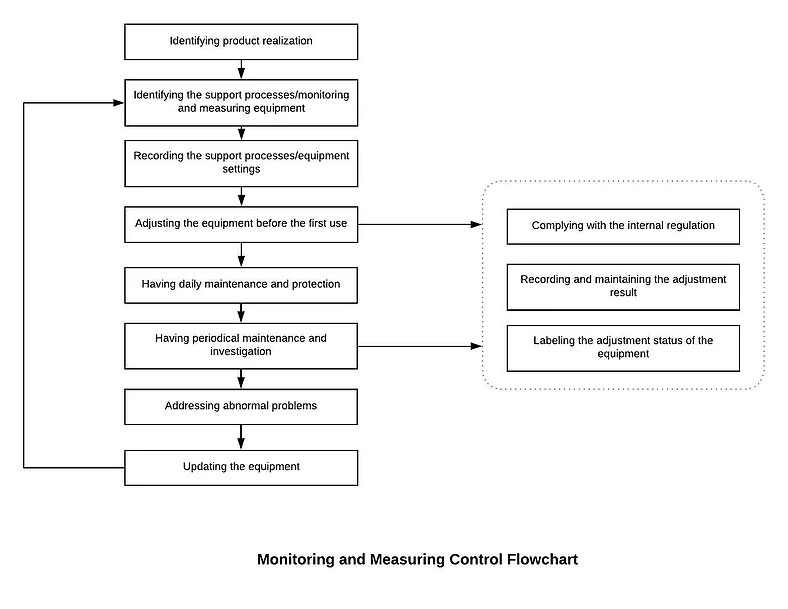 7.1.5.1 Establish and maintain the Monitoring and Measurement Control Procedure. Identify monitoring and measurement requirements and configure appropriate monitoring and measurement equipment.
7.1.5.1 Establish and maintain the Monitoring and Measurement Control Procedure. Identify monitoring and measurement requirements and configure appropriate monitoring and measurement equipment.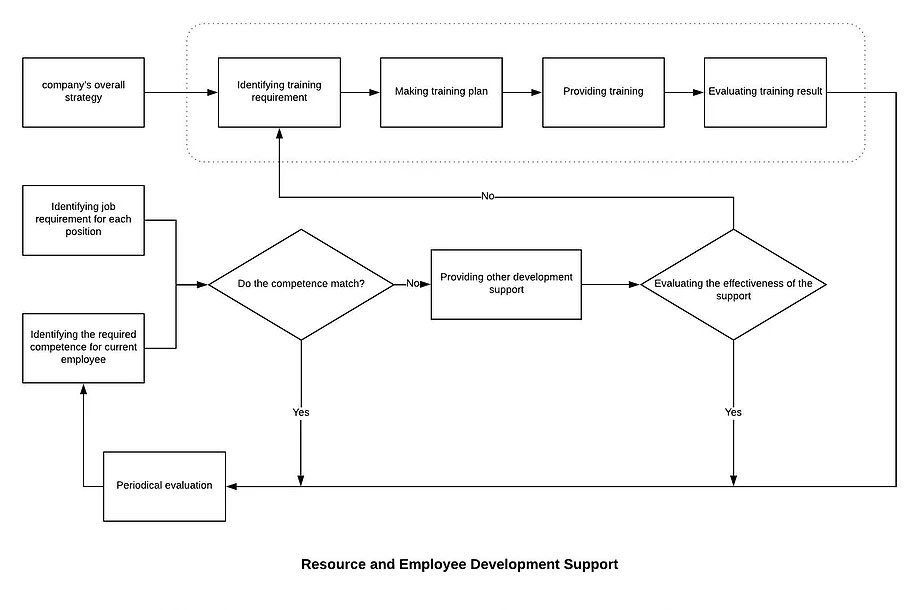 Our Management will
Our Management will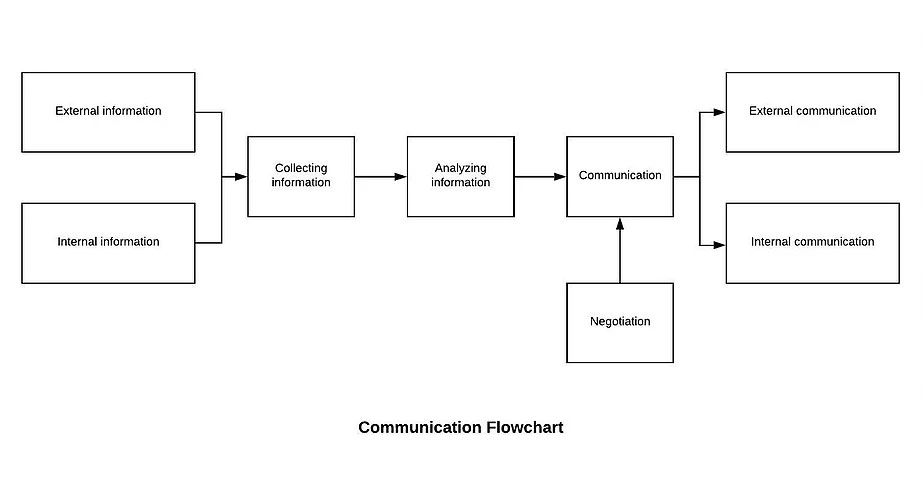 The company determines the internal and external communications relevant to the quality management system, including:
The company determines the internal and external communications relevant to the quality management system, including: